Useful Publications
Evaluating Need for Foliar Fungicides
Wheat Variety Disease and Insect Ratings
Foliar Fungicide Efficacy Ratings
Identifying Rust Diseases of Wheat and Barley
Variety Response
| Stripe Rust Resistance Ratings | ||||
| Susceptible | Moderately Susceptible | Intermediate | Moderately Resistant | Resistant |
| Avery | Brawl CL+ | Hatcher | Antero | Joe |
| AP503CL2 | KanMark | LCS Mint | Overland | "Larry" |
| Armour | PostRock | Robidoux | SY Sunrise | LCS Chrome |
| Byrd | Winterhawk | SY Wolf | Oakley CL | |
| Danby | WB 4458 | SY Monument | ||
| Denali | WB-Cedar | T-158 | ||
| TAM 111 | WB-Grainfield | "Tatanka" | ||
| TAM 112 | TAM 114 | |||
| WB 4721 | ||||
Development of Stripe Rust
This is how stripe rust looks, just prior to the pustules erupting from the leaf surface (lower leaf). There are lighter colored eliptical areas of the leaf surface. They follow the veins of the wheat leaf.
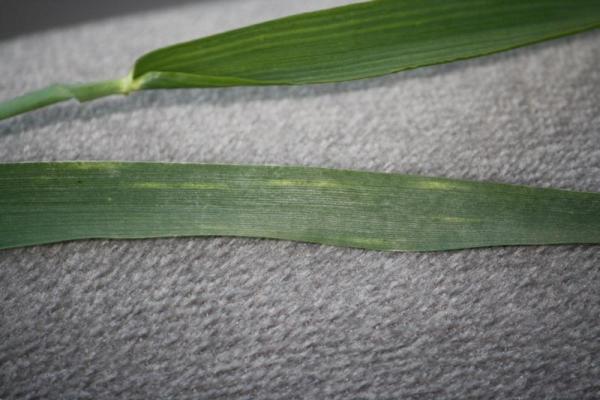

This is stripe rust as rust pustules begin to appear the leaf surface. There pustules are shiny and have emerged from the leaf surface in the last 24-48 hours.

At this time, if fingers are ran over the leaf surface, they will not turn orange. This is because the pustules are not actively sporulating (releasing spores).
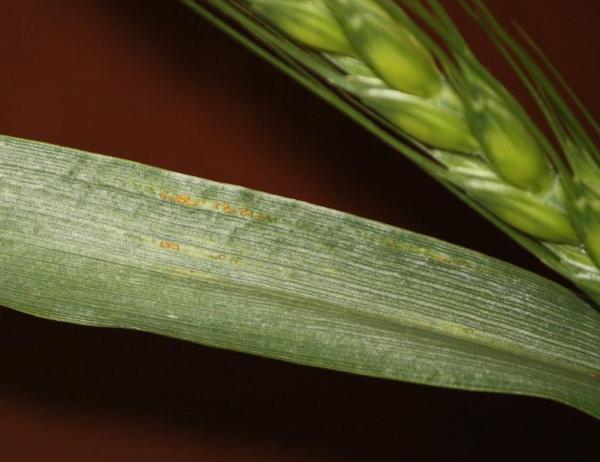

This is stripe rust, after pustules appear and spores erupt from the leaf surace. The spores are a light orange color and are in long eliptical shapes on the upper surface of the leaf. If your finger is ran over the surface, orange residue will appear on your skin. Bumps (from erupting spores) will also be visible on the leaf surface. To see these, fold leaf over your finger and look at it while running over the finger in the light.
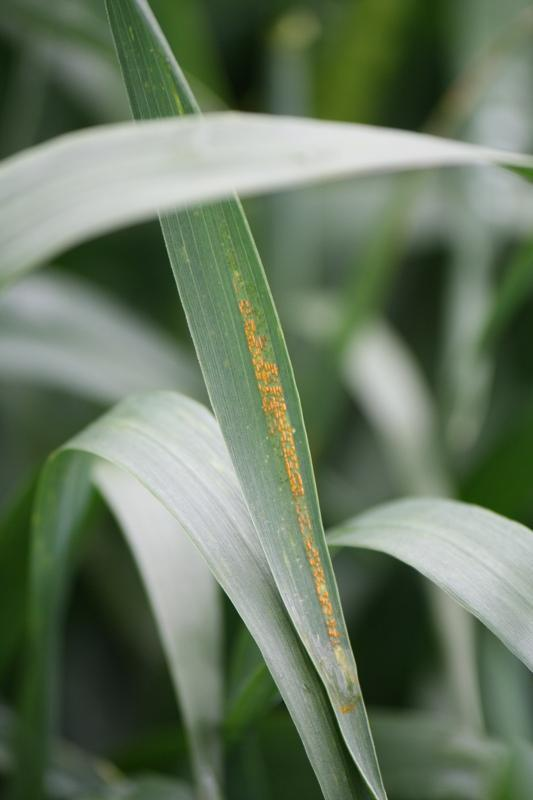

Treatment for this disease are fungicides. Click on the publication below to learn about fungicide treatments, rates, efficacy ratings and pre harvest intervals for treatments.
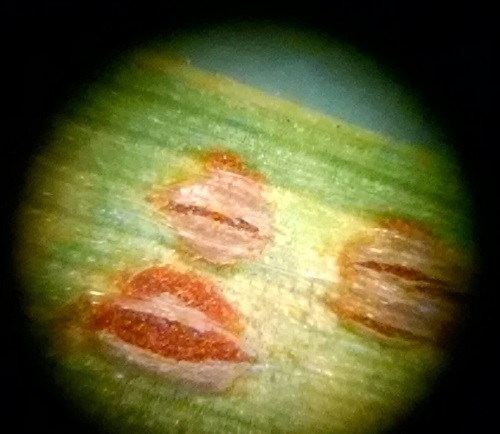
Stripe rust close up
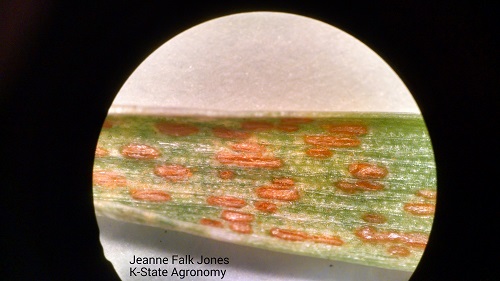
Stripe rust-advanced close up
Are fungicides helping slow and stop the development of stripe rust?
Erick DeWolf, Extension Plant Pathology
I visited some fields in south central Kansas this week that were sprayed with fungicide about a week ago. The fungicides appear to have stopped the development of stripe rust. The stripe rust lesions were now tan and dry instead of the normal bright yellow color of active stripe rust. This indicates to me that the fungicide had killed the stripe rust fungus and stopped the production of new spores.
